Strategy ONE
Defining Graph Matrix widgets
A Graph Matrix widget allows you to quickly analyze various trends across several metric dimensions. You can use the widget to assess questions such as "How are sales comparing vs. forecast, by time and region?".
The Graph Matrix widget consists of several area graphs that display current values. Each area graph also has a line graph above it to show forecasted values. One graph is displayed for every combination of elements from the attributes on the rows and columns of the Grid/Graph that contains the widget. For example, in the widget below, the rows of the Grid/Graph contain the Category attribute elements and the columns contain the Region attribute elements. Twelve graphs are displayed because data exists for four regions and three categories of products.
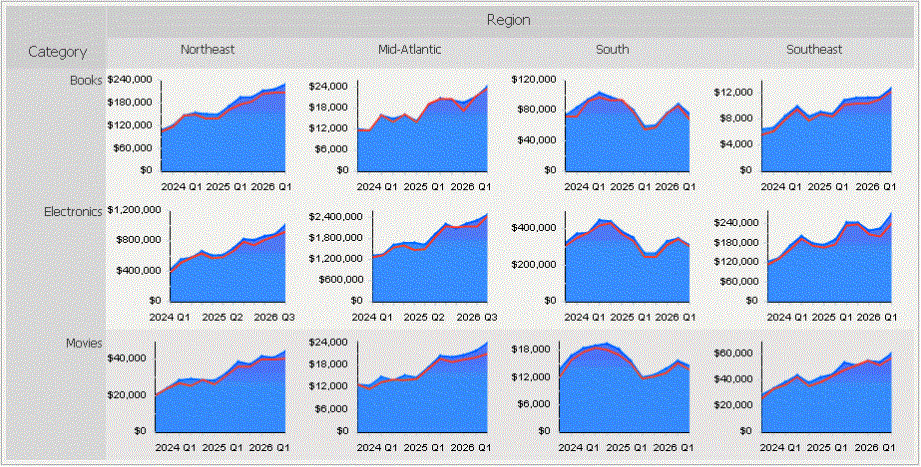
A separate area graph is produced for each combination of region and product category. For example, one area graph focuses solely on electronics product figures in the Northeast region. Values in that graph are plotted across quarter (on the X-axis) and revenue (on the Y-axis). The line graph at the top of the area graph represents revenue forecast metric values, or the amount of revenue the company predicted it would generate.
You can maximize a specific area graph by double-clicking it. The graph opens in a new window, as shown below.
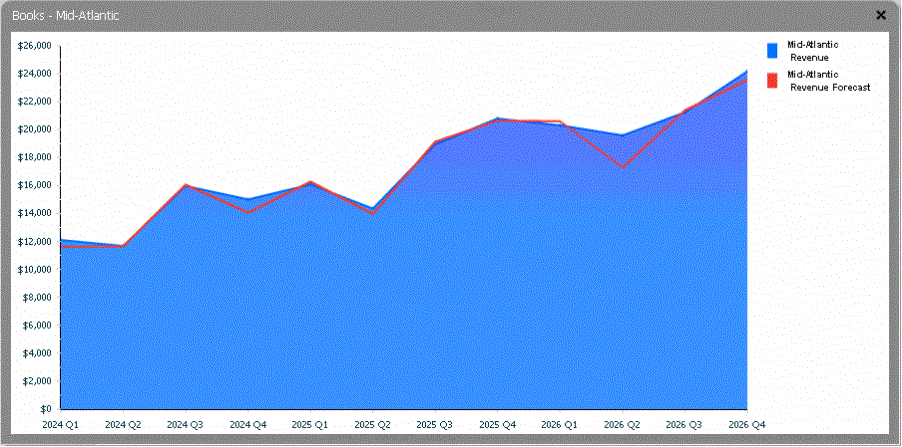
Each area graph in a Graph Matrix widget has the following characteristics, as shown above.
-
x
-
The X-axis provides the time scale. For example, the X-axis can represent weeks, quarters, or years.
-
The Y-axis provides the metric values. For example, the Y-axis can represent revenue, profit, or units sold.
-
The area graph shows the current values, allowing you to see how values changed over time. The area graph represents the values of the first metric on the report.
-
The line graph at the top of the area graph shows the predicted, or forecasted, values. The line graph represents the values of any additional metrics on the report.
-
The black reference line in the area graph (not displayed above) shows the average for only the specific graph you are looking at.
-
The red reference line in the area graph (not displayed above) shows the average metric value for all of the graphs in the same row of the Graph Matrix widget. This allows you to easily compare one graph in the widget to another.
Data requirements for a Graph matrix widget
To successfully create a useful Graph Matrix widget that can be used to analyze data, you must first correctly define the Grid/Graph. To do this, you must place report objects such as attributes and metrics on the Grid/Graph. The report objects and their placement on the Grid/Graph determine whether the Graph Matrix widget can be successfully generated and can display data.
The data requirements for a Graph Matrix widget are described below:
-
At least two attributes on the rows. The first (left-most) attribute on the rows, and the second, third, fourth, and so on, provide the row headers in the widget. The last (right-most) attribute on the rows provides the X-axes of the graphs. This attribute, which is generally time-based, is used to drive the time series of the graphs.
-
At least one attribute on the columns, unless the rows contain at least three attributes. The first (left-most) attribute on the columns provides the column headers in the widget. These values are used to slice the data, grouping it by the attributes on the columns.
-
Any additional attributes on the columns produce separate line graphs within each area graph in the widget.
-
-
At least one metric on the columns, to the right of or below the attribute. The first metric is depicted as the colored series in the area graphs.
-
Any additional metrics are depicted as forecast line graphs in each area graph.
-
A Graph Matrix widget does not need a separate selector to allow a user to interact with it. However, you can use a Graph Matrix widget as a selector. For an example and more information, see Using Graph Matrix widgets as selectors.
For instructions to create a widget, see Creating widgets. For information on formatting a Graph Matrix widget, see Formatting Graph Matrix widgets.
