Strategy ONE
Defining selectors
Selectors provide Report Services (RS) dashboards with interactivity, allowing each user to change how he sees the data. A selector can change panels in a panel stack, another selector, the focus of a Grid/Graph, or a dynamic text field (a text field that is a reference to an object on a report) in a panel stack.
When you add a selector to a document, you must define how it looks and what it controls. The following properties define a selector:
-
DHTML style is how the items in the selector are displayed in Editable, Interactive, and Express Mode in MicroStrategy Web. (Items are the elements, metrics, or panels that are listed in the selector. The user selects an item to change the panel or Grid/Graph.) The style options are:
-
Button Bar (use to create tabs in your document)
![]()
-
Check Boxes
![]()
-
Drop-down

-
Link Bar (use to create tabs in your document)
![]()
-
Listbox

-
Qualification (available only for metric condition selectors; allows users to complete the metric qualification)
-
Radio Buttons
![]()
-
Slider: The most effective selector for browsing data in a graph; also available for metric condition selectors.
-
Flash Style is how the selector is displayed in Flash Mode in MicroStrategy Web if it is an interactive Flash-only selector. The options are listed below:6y
-
Automatic: The default, which uses the DHTML style (described above) for Flash Mode.
-
Fish Eye Selector: An interactive style of selector that is displayed only in Flash Mode. It magnifies an item when a user hovers the cursor over it. This style of selector is useful because it allows a user to choose from a large list of elements without having to see all of the elements displayed at the same time. Any item that a user hovers over or selects remains magnified, while the remaining items are minimized and hidden from view.
-
Since a Fish Eye Selector is displayed only in Flash Mode, determine how the selector is displayed in non-Flash modes by specifying a DHTML style (described above).
-
For more information about creating this type of selector, see Creating Fish Eye Selectors.
-
-
Date Selection: An interactive style of selector that is displayed only in Flash Mode. It is a calendar selector that allows you to select which dates you want to see data about in a document. You are able to see all of the dates of each month in the widget, which allows you to be able to select dates more easily.
-
Since a Date Selection selector is displayed only in Flash Mode, determine how the selector is displayed in non-Flash modes by specifying a DHTML style (described above).
-
For more information about creating this type of selector, see Creating Date Selection widgets.
-
-
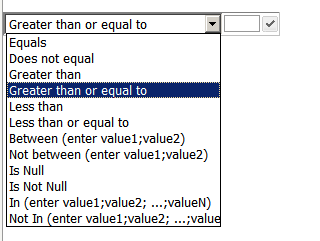
Action Type determines whether the selector displays elements, metrics, metric conditions (such as "greater than $5,000"), or panels.
-
Source is the attribute, custom group, or consolidation whose elements are displayed in the selector (for an element selector) or the metric whose values are qualified on (for a metric condition selector).
-
Selection Type determines whether the selector includes or excludes the selected items from the target. It is available only for element selectors and metric condition slider selectors. For example, the attributes that a user chooses in the selector can display in the target, or they can be hidden. For instructions to specify the selection type, see Determining whether the selector includes or excludes data: selection type.
-
Qualify on determines whether the selector filters metric values or rank, and is available only for metric condition selectors. The options are:
-
Value filters the metric's values.
-
Rank Highest ranks the metric's values in descending order, and then filters by rank. For example, Rank Highest=2 displays the two highest values.
-
Rank Lowest ranks the metric's values in ascending order, and then filters by rank. For example, Rank Lowest=2 displays the two lowest values.
-
Rank % Highest ranks and filters by the number of metric values (or rows) in the target, in descending order. For example, if the target Grid/Graph contains eight items, the Rank % Highest =25 displays the two highest values.
-
Rank % Lowest ranks and filters by the number of metric values (or rows) in the target, in ascending order. For example, if the target Grid/Graph contains eight items, the Rank % Lowest =25 displays the two lowest values.
-
If a title bar is displayed for the metric condition selector, a user can change this setting.
-
-
Targets are the Grid/Graphs, panel stacks, and/or other selectors that the selector affects.
-
If targets are automatically maintained in the layout, attribute, metric, and metric condition selectors automatically target all Grid/Graphs and panel stacks that are in the same panel or document section as the selector.
-
If targets are not automatically maintained, you must manually select the targets when you create selectors.
-
You must always select the target for panel selectors, regardless of whether targets are automatically maintained.
-
To choose another selector as the target of this selector, you must disable automatic target maintenance and manually select the target. You can keep automatic target maintenance if you can place the target selector on a panel in the same document section as the source selector; the source selector will automatically target that panel stack.
-
For instructions to disable automatic target maintenance, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of automatic and manual target selection, see Automatically maintaining targets for selectors.
-
