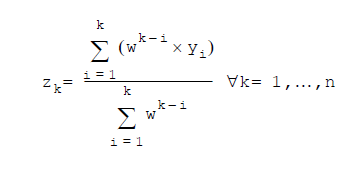Strategy ONE
ExpWghRunningAvg (Exponential Weighted Running Average)
ExpWghRunningAvg allows you compute a running average while placing more or less emphasis on recent data than on past data. The calculation can restart based on an attribute specified in the function parameters.
Syntax
ExpWghRunningAvg <BreakBy, SortBy> (Argument, Rate)
Where:
BreakByis the attribute indicating where the calculation restarts.SortByis the attribute or metric by which the data is sorted.Argumentis a metric representing a list of numbers.Rateis a positive real number specifying the base weight applied to each argument value. In the calculation, exponents are sequentially applied to the rate value. Assign a rate of less than one to give more emphasis to more recent data; assign a rate of greater than 1 to give greater emphasis to past data.
Expression
Where:
k= row numberyi= metric value at the ith rowm= window size or the row number, whichever is smallern= number of rows-
w= the base weight applied to each value, which is determined by theRatevalue in the function, as described in the function syntax details aboveRows with null values are excluded from the calculation.
Example
This example uses small numbers to demonstrate the calculation for the exponential weighted running average (ExpWghRunningAvg) function. For example, you have a list of values (32, 8, 5), with 5 being the most recent value, and you assign a rate of .5.
| values | EWR average | calculation |
|
32 |
32 |
32(.5)0 / (.5)0 = 32(1)/1 = 32
|
|
8 |
16 |
8(.5)0 + 32(.5)1 / (.5)0 + (.5)1 = 8(1)+ 32(.5) / 1+.5 = 8+16 / 1.5 = 16 |
|
5 |
10 |
5(.5)0 + 8(.5)1 + 32(.5)2 / (.5)0 + (.5)1 +(.5)2 = 5(1)+ 8(.5)+ 32(.25) / 1+ .5 + .25 = 5 + 4 + 8 / 1.75 = 10 (rounded from 9.71) |