Strategy ONE
Formatting HTML containers
Before you begin
You should be familiar with the different types of HTML container, iFrame and HTML text. The iFrame type contains the URL of a website, while the HTML text type contains HTML tags that are rendered in MicroStrategy Web. For examples and a more detailed explanation of the differences, see Displaying HTML content in a document: HTML containers.
When you insert an HTML container into a document, its formatting is initially determined by the control defaults. However, you can then change any of the formatting options for the new HTML container.
Formatting options, such as borders and background colors, apply to the HTML container itself, not to anything placed inside the container. Examples for formatting the HTML container include 3D borders and background colors, as shown in the first sample below, and drop shadows, as shown in the second sample.

HTML container formatting options do not affect what the HTML container displays (either the text or the website).
The following list provides some useful formatting suggestions for all HTML containers.
-
Create a border around the HTML container. To create a basic border, click the Border icon in the Formatting toolbar, and select the border type. For details on all border formatting options, see Formatting HTML containers using the Property List or Formatting HTML containers using the Format Objects dialog box.
-
Make an HTML container appear three-dimensional, like a button, with the 3D effect. For detailed instructions, see Applying 3D effects.
-
"Float" the HTML container above the background by using a drop shadow. For detailed instructions, see Applying drop shadows.
-
Display pop-up text when a user positions the cursor over the HTML container in MicroStrategy Web. The pop-up text is called a tooltip, and can provide extra information, such as a description of a website. For an example of a tooltip, and instructions to create them, see Creating pop-up tooltips.
For an HTML container that displays formatted text using HTML tags, you can also format the HTML container in the following ways:
-
Allow the content behind the HTML container to show through by setting the backstyle of the HTML container to transparent. You can also allow a fill color to cover what is behind the HTML container by setting the backstyle to opaque. For an example and instructions, seeApplying transparent or opaque backstyles.
-
Select the background color of the HTML container by setting the backcolor. To set the background color, click the Fill icon in the Formatting toolbar, and select the color from the drop-down menu. For details on all background formatting options, see Formatting HTML containers using the Property List or Formatting HTML containers using the Format Objects dialog box.
-
Create a gradual color change by blending two colors using gradient colors. For an example and instructions, see Applying gradient colors.
-
Format the font of the text displayed by the HTML container. Font format options include the font type, size, and color, as well as whether it is bold or italicized. For more detailed instructions, see Formatting HTML containers using the Property List or Formatting HTML containers using the Format Objects dialog box.
This font formatting is overwritten by font formatting provided in the HTML code, as explained below.
The formatting of the content inside the HTML container is determined by either the HTML tags or the website displayed by the URL. For an HTML container that contains HTML tags, any font formatting not specified in the HTML tags is provided by the MicroStrategy formatting options.
For example, the following HTML container, shown in Design View, contains HTML tags. The HTML tags do not apply to the text until the document is displayed in MicroStrategy Web. The HTML tags format the first line as a heading 2. The second line is displayed in a blue Courier font by the HTML tags. The third line does not use any HTML tags. Notice that the Property List for the HTML container indicates that the object uses a black Tahoma font (the Forecolor property is the color of the font).

The same HTML container is shown below in Express Mode in MicroStrategy Web. Notice that the second line is displayed in a blue Courier font (as defined by the HTML tag), unlike the black Tahoma font of the other lines (which use the font properties defined for the HTML container). The first line is bold and displayed in a larger font than the other lines because of the h2 HTML tag. The other lines display in the font size indicated for the HTML container.

The font formatting for an HTML container applies only to HTML containers that use HTML tags. For example, the following HTML container is an iFrame, using a URL to display a website. The font is defined to display as an italicized gray.
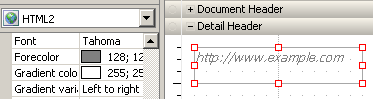
The same HTML container is displayed below in Express Mode in MicroStrategy Web. The website determines how the text is displayed. In this case, it is black and not italicized.

You can change the formatting options for an HTML container as described below:
-
For all formatting options and properties, use the Property List. Formatting options include font, alignment, borders (including 3D borders and drop shadows), and colors, including gradient colors (two-color combinations). The general and layout properties include the properties that define the text field, such as name, position, size, and HTML code/URL.
-
For easy access to basic formatting options, format the HTML container using the Formatting toolbar. Basic formatting options are fonts, colors, and basic borders.
-
For easy access to border, background fill, and font color, use the right-click options.
-
For font, alignment, border, and color options, including gradient colors, 3D borders, and drop shadows, use the Format Objects dialog box.
The Property List is the easiest to use, as it contains all the options of the other interfaces on the same screen as the Layout area.
