Strategy ONE
Conditional metric example
The following report compares the paid salaries and bonuses of different departments. It uses a prompted report filter on year; the report sample below contains 2023 data.
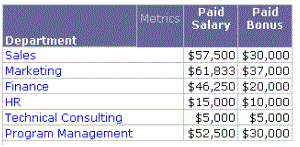
The Paid Salary metric sums the Compensation Cost fact and has a condition, the Base Salary filter. This filter qualifies the Compensation Item attribute for Base Salary. The metric definition is shown below:
Sum([Compensation Cost]) {~+}
<[Base Salary]>
Notice that the filter name is placed between angle brackets (< >). (Additional symbols are described in Metric Editor Formula tab: Metric level property symbols.) The Paid Bonus metric is similar to Paid Salary, except its condition is Regular Bonus, which filters the Compensation Item attribute for Bonus. The metric definition is shown below:
Sum([Compensation Cost]) {~+}
<[Regular Bonus]>
An additional requirement for this report is a comparison of the bonus amount to the salary amount. This is easy to do by combining the conditional metrics. Create a compound metric that divides the Paid Bonus metric by the Paid Salary. The metric definition is shown below:
([Paid Bonus] / [Paid Salary])
The new metric does not have its own condition; the condition on each of the constituent metrics is applied only to that metric. For a more detailed description of compound metrics, including examples and procedures, see Creating compound metrics.
