Strategy One
Retrieve Data in UTF-8 on Windows
According to our performance tests, switching the Windows operating system encoding from UTF-16 to UTF-8 causes the data processing time to drop about 10% to 15%. See the performance in the following table.
| UTF8 | UTF16 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transfer Time (s) | Transfer and Processing Time (s) | Cube Size (GB) | Memory (GB) | Transfer Time (s) | Transfer and Processing Time (s) | Cube Size (GB) | Memory (GB) | |
| Trial 1 | 0:06:45 | 0:07:38 | 12.0 | 10.1 | 0:06:27 | 0:08:08 | 12.0 | 10.7 |
| Trial 2 | 0:05:54 | 0:06:46 | 12.0 | 10.6 | 0:06:23 | 0:08:14 | 12.0 | 10.2 |
| Trial 3 | 0:06:45 | 0:07:38 | 12.0 | 10.6 | 0:06:26 | 0:08:17 | 12.0 | 10.5 |
| Average | 0:06:28 | 0:07:21 | 12.0 | 10.4 | 0:06:25 | 0:08:13 | 12.0 | 10.5 |
Setting the Windows operating system encoding to UTF-8 can also prevent the following error from occurring:
QueryEngine encountered error: MBase::UTF8ToWideChar: Invalid continuation octet 0x74.
- Windows
- Developer
- Log into Windows 10 or Windows Server 2019 and above.
- In the left bottom corner, click Start.
- Search for Control Panel and open it.
- Click Clock and Region.
-
Click Region.
-
Go to the Administrative tab and click Change system locale.
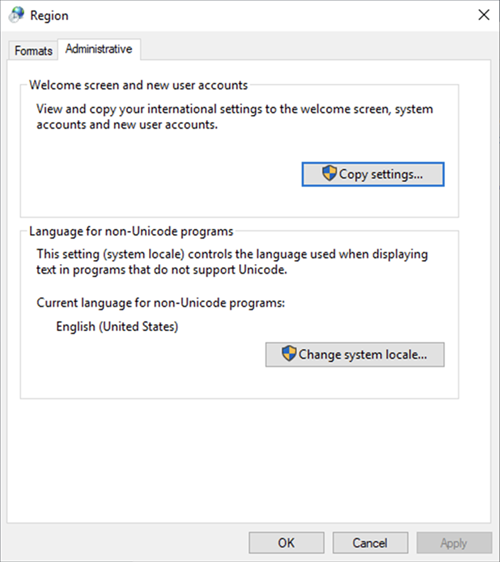
-
Select the Beta: Use Unicode UTF-8 for worldwide language support checkbox and click OK.
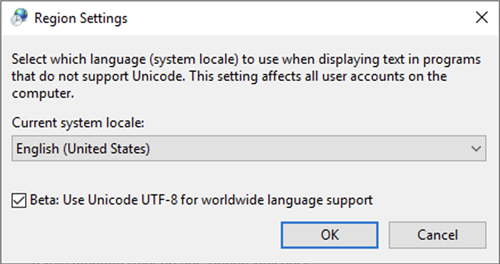
-
Click Restart now.
- Create an ODBC DSN.
- Open MicroStrategy Developer.
- Go to Administration > Configuration Managers.
-
Right-click Database Instances > New > Database Instance.

-
Enter a database instance name and connection type and click OK.
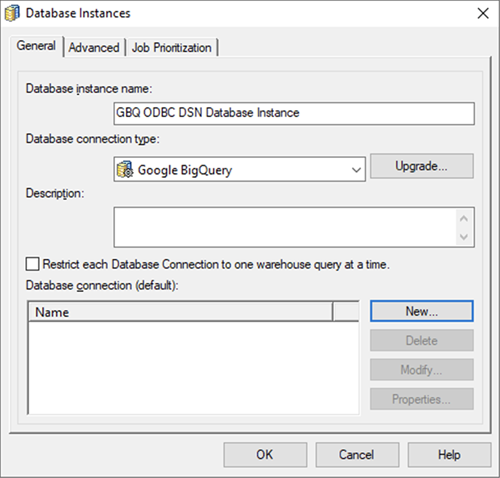
-
Enter a database login, login ID, and password and click OK.
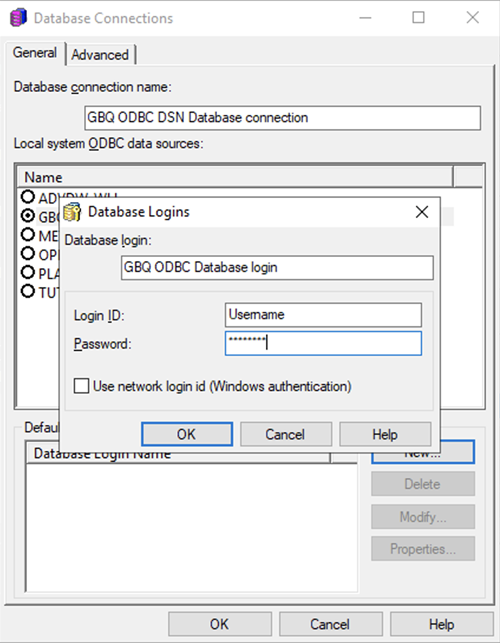
-
Go to the Advanced tab.
-
Under the Character set encoding for Windows drivers setting, select UTF-8 and click OK.

-
Click OK.
