Strategy One
Interacting with a Document: Selectors
Selectors provide dashboard-style documents with interactivity, allowing each user to change how they see the data. A selector can change panels, the focus of a grid or graph report, or dynamic text fields (a text field that is a reference to an object on a report) in a panel stack, as described below.
Selectors allow you to:
-
Flip through the panels in a panel stack. A panel stack is a collection of panels, which allow you to see different predefined views of data in the same document.
For example, each panel can display a different grid, and the selector allows you to choose which panel, and thus which grid, to view.
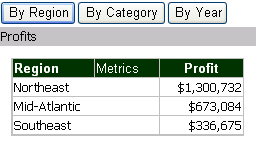
-
Display different metrics; different attributes; or different elements of attributes, custom groups, or consolidations in a grid or graph report.
For example, a grid contains Region, Call Center, Year, and various metrics, as shown in the example below. This particular selector allows you to select which regions to display on the grid. You can therefore slice or filter the grid by the selected region or regions. Similarly, a selector can allow you to select which metrics to display. All regions and employees would be displayed, but with only the metrics chosen in the selector.
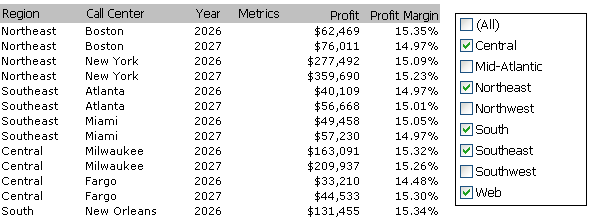
-
Filter data based on a metric's values. This type of selector can be either of the following styles:
-
A slider, which you move to select the minimum and maximum values to display. For example, a document contains a grid with Region and the Revenue, Cost, and Profit metrics. A selector displays the range of revenue values, and you can move the slider to select the minimum and maximum revenue to display or to hide.
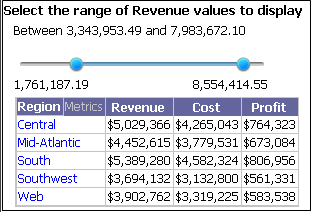
-
A qualification, which you complete to filter the metric's values. This type of metric condition selector allows you to select the operator (equals, greater than, between, and so on) and to type the value to filter on. For example, given the same regional grid described above, you could display only the revenue values greater than $5,000,000 or only the top-ranking 5 regions in term of revenue.
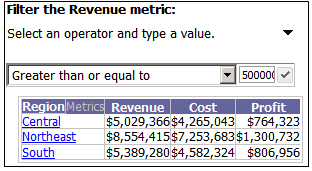
The document designer can include a title bar on the selector. If the title bar is displayed, you can also select whether to filter on the metric values or rank.
-
-
Filter another selector. For example, a document contains a grid with Subcategory and Item, filtered to display only the Books category. The document also includes two selectors. One selector displays the subcategories in the Books category (the Subcategory selector), while the other selector contains a list of individual books (the Item category). Both selectors target the grid, to display data for the selected Subcategory and Item. The Subcategory selector targets the Item selector, filtering the Item selector to display only the books in the subcategory chosen in the Subcategory selector. For example, if you select Literature from the Subcategory selector, the Item selector is updated to display only books that fall under the Literature subcategory, instead of displaying a long list of every available book. This is shown below:
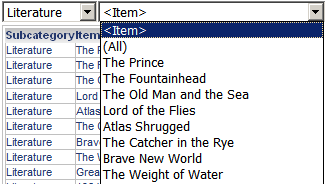
-
Display different elements of attributes, custom groups, or consolidations in a panel stack using dynamic text fields. A dynamic text field is a text field populated by the dataset; it is essentially a reference to an object on a dataset, in this case, a report.
For example, a panel contains the dynamic text fields Region and Revenue from the Basic Report dataset. The selector allows you to choose which region to display on the panel. When you select Mid-Atlantic from the drop-down list of the selector, Mid-Atlantic and its revenue amount are displayed on the panel stack.
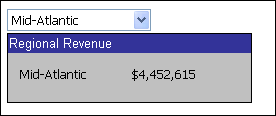
A selector can target multiple objects. The same selector can control both a grid and dynamic text fields on the same panel. As described in the "filter another selector" example above, the same selector can target both a Grid/Graph report and another selector.
You can reset all the selectors and groups on the document to their initial values, without re-executing the document. This is helpful if you want to start over and make different selections. To reset, click the menu icon ![]() on the right, and select Reset Selections.
on the right, and select Reset Selections.
Including or Excluding Data Using a Selector
An element selector or a metric condition slider selector can include or exclude the selected data. (An element selector displays different elements of attributes, custom groups, or consolidations; a metric condition slider displays a slider to filter metric values or rank.) For example, the attributes that you choose in the selector can display in the target, or they can be hidden. If the selector title bar is displayed, you can change between including or excluding the selections.
The following document contains an element selector that displays regions and targets a grid report. You can select regions and by default they are displayed rather than hidden in the grid, as shown below.
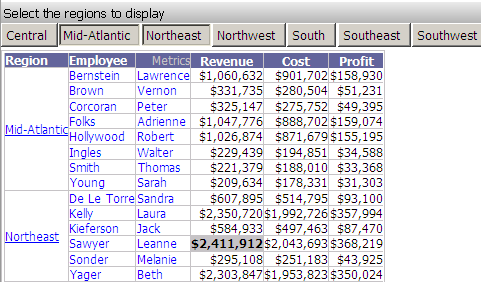
By clicking in the title bar, you can switch to hiding the selected regions. Notice in the image shown below that Northeast and Northwest are now crossed out. (Only a portion of the full grid is shown below.)
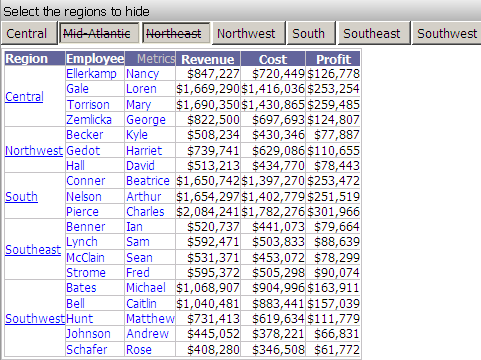
Related Topics
Using a Grid or Graph as a Selector
How Drilling and Selectors Work Together
How Links, Drilling, and Selectors Work Together
How to Use Selectors to Change the Data Displayed in a Document
