Strategy ONE
Escribir un script de origen de datos Python
Iniciar sesión en MicroStrategy ONE Actualización 11: para usar un origen de datos Python, debe escribir un script Python que se usará como conexión para el origen de datos.
Funciones del script de origen de datos
Debe utilizar las tres funciones siguientes en el script de origen de datos:
-
browse()Copiardef browse():
"""
Description: retrieve the catalog information.
Input: no input is needed for this function.
Return: the result is returned as a dict object.The keys of the dict should be
table names of the python data source, and the values are normalized in Pandas
DataFrame format. Each DataFrame value will contain a table's column infos.
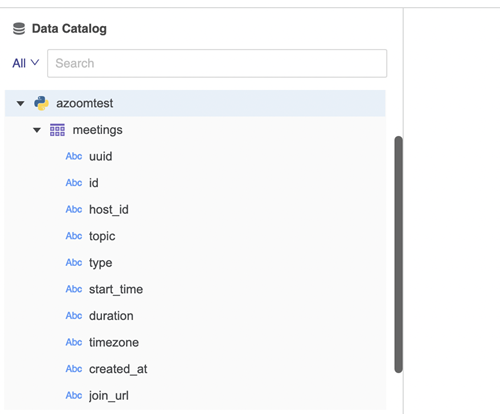
"""Esta función de exploración se activa cuando un usuario intenta conectarse a un origen de datos a través de un conector Python. Cuando el origen de datos se conecta, devuelve toda la información de catálogo del origen de datos. Los nombres de tabla y las columnas se muestran bajo el origen de datos.
-
preview()Copiardef preview(table_name, row_limit):
"""
Description: get partial data for preview, data refine and schema change
Input: there are 2 parameters for preview.
- table_name: a table name should be selected if someone want to preview
the table.
- row_limit: the row limitation is used to define the scale when only
partial data is retrieved during the preview.
Return: the result is returned as a Pandas DataFrame format object. Only the
"row_limit" rows would be returned in the DataFrame object.
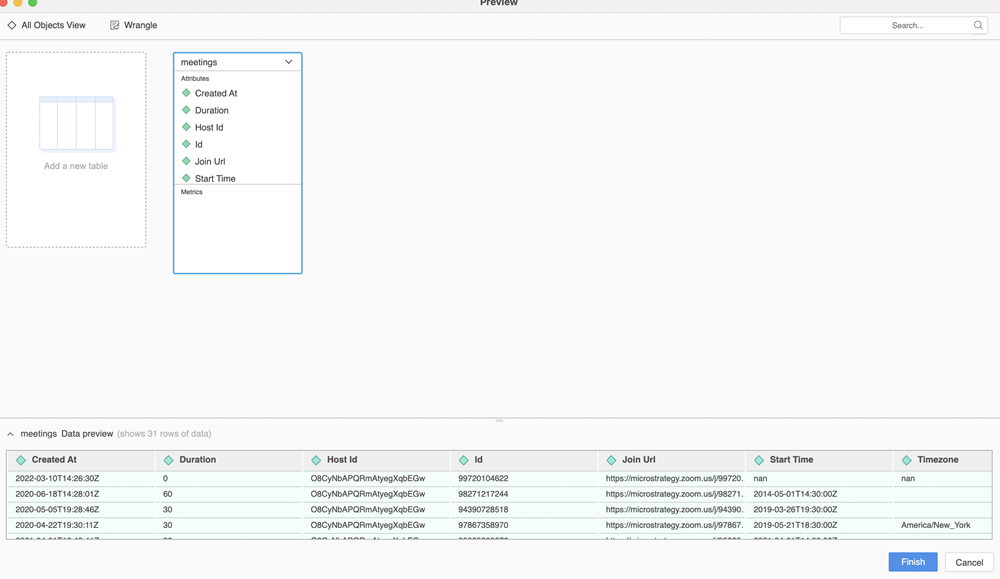
"""La función de vista previa se activa cuando el usuario hace doble clic para añadir una tabla o hace clic para ver la vista previa de una tabla.
-
publish()Copiardef publish(table_name):
"""
Description: get the data published and stored the data into the cube
Input: the table_name parameter is needed to define witch table should
be published.
Return: the result is returned as a Pandas DataFrame format object. All
data needs to be returned for publishing.
"""La función de publicación se desencadena cuando un usuario hace clic en Guardar para publicar un cubo. Todos los datos de la tabla se han recuperado para que el usuario los consuma.
Para más información acerca de Pandas DataFrame, consulte 10 minutos para pandas.
Ejemplo de script de origen de datos
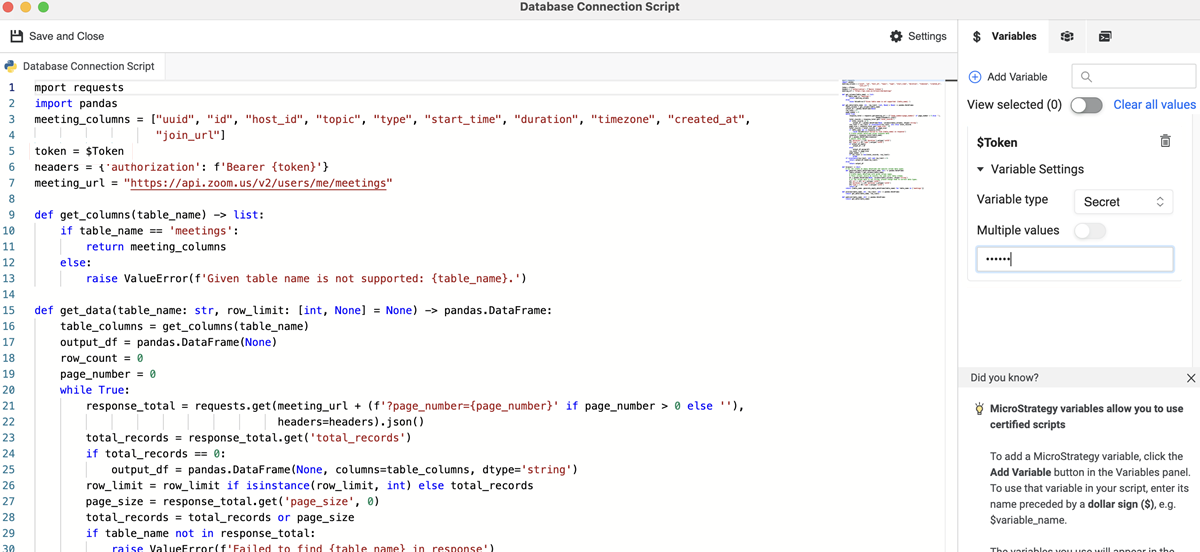
Consulte el siguiente ejemplo de conector de zoom. Los usuarios pueden conectarse a los recursos de Zoom con las API en un origen de datos de Python para recuperar los datos que deseen. El ejemplo incluye una variable llamada Token en el script de origen de datos para la autenticación.
import requests
import pandas
meeting_columns = ["uuid", "id", "host_id", "topic", "type", "start_time", "duration", "timezone", "created_at",
"join_url"]
token = $Token
headers = {'authorization': f'Bearer {token}'}
meeting_url = "https://api.zoom.us/v2/users/me/meetings"
def get_columns(table_name) -> list:
if table_name == 'meetings':
return meeting_columns
else:
raise ValueError(f'Given table name is not supported: {table_name}.')
def get_data(table_name: str, row_limit: [int, None] = None) -> pandas.DataFrame:
table_columns = get_columns(table_name)
output_df = pandas.DataFrame(None)
row_count = 0
page_number = 0
while True:
response_total = requests.get(meeting_url + (f'?page_number={page_number}' if page_number > 0 else ''),
headers=headers).json()
total_records = response_total.get('total_records')
if total_records == 0:
output_df = pandas.DataFrame(None, columns=table_columns, dtype='string')
row_limit = row_limit if isinstance(row_limit, int) else total_records
page_size = response_total.get('page_size', 0)
total_records = total_records or page_size
if table_name not in response_total:
raise ValueError(f'Failed to find {table_name} in response')
# Create pandas dataframe using response data
response = response_total[table_name]
df = pandas.DataFrame(response)
# Adjust data types
df['duration'] = df['duration'].astype('int32')
df['type'] = df['type'].astype('int32')
if output_df.empty:
output_df = df
else:
output_df.merge(df)
row_count += page_size
page_number += 1
if row_count >= min(total_records, row_limit):
break
if isinstance(row_limit, int) and row_limit > 0:
return output_df.head(row_limit)
else:
return output_df
def browse() -> dict:
# You can create an empty dataframe and specify column data types.
def generate_empty_dataframe(table_name: str) -> pandas.DataFrame:
table_columns = get_columns(table_name)
# Create empty dataframe with given column names.
# These columns should be exactly the same with table schema.
df = pandas.DataFrame(None, columns=table_columns, dtype='string')
# If the column data is not string, please change them to correct data types.
df['id'] = df['id'].astype('int64')
df['duration'] = df['duration'].astype('int32')
df['type'] = df['type'].astype('int32')
return df
return {table_name: generate_empty_dataframe(table_name) for table_name in ['meetings']}
def preview(table_name: str, row_limit: int) -> pandas.DataFrame:
return get_data(table_name, row_limit)
def publish(table_name: str) -> pandas.DataFrame:
return get_data(table_name)