Strategy ONE
Binomial distribution
Returns either the binomial probability or the cumulative binomial probability of variables n and p. This function is used in cases in which:
- There is a fixed number of tests
- Each test can only result in either success or failure (binary)
- Tests are independent of all other tests
- The probability of success is constant, for example, to calculate the probability that two out of the next three babies will be male
Syntax
BinomialDistribution <Cumulative> (x, n, p)
Where:
x is the number of successes.
n is the number of tests.
p is the number indicating the probability of a success in each trial.
Cumulative is a logical value that determines the form of the function.
- If
Cumulative=0, it computes the Cumulative Binomial probability. - If
Cumulative=1, it computes the Binomial probability.
Expression
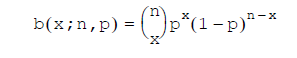
For the binomial probability:
Where:
is Combine(n, x).
The cumulative binomial distribution is:
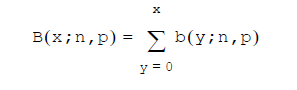
Usage Notes
If x or n is not an integer, it is truncated.
The following conditions are invalid:
- One of the arguments is nonnumeric.
- x > n
- x< 0
- p < 0 or p > 1
