Strategy ONE
Covariance
Covariance is used to examine the relationship between two data sets. For instance, the covariance could be used to examine whether an increase in income is related to higher education levels. A covariance greater or less than zero indicate a relationship, while a value of zero indicates no relationship.
To determine the covariance of two values while applying a weight to the comparisons, see WeightedCov (weighted covariance).
Covariance is similar to Correlation and Pearson, which also describe the relationship between two data sets. While Covariance describes the relationships with positive or negative values, Correlation and Pearson normalize these positive or negative values to a range between -1 and 1.
Syntax
Covariance <FactID> (Argument1, Argument2)
Where:
Argument1 and Argument2 are facts or metrics representing lists of values.
FactID is a parameter that forces a calculation to take place on a fact table that contains the selected fact.
Expression
In the expression that follows:
Argument1= XArgument2= Y
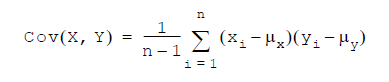
Where:
= average value of x
= average value of y
Usage Notes
The following conditions are invalid:
- Argument1 and Argument2 do not contain the same number of data points.
- Either value set is empty.
