MicroStrategy ONE
Creating a Conditional Metric
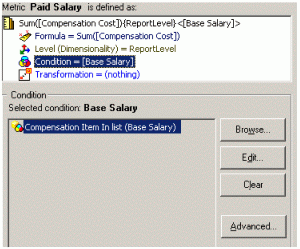
Use the Metric definition area of the Metric Editor to set the metric condition. This area is split into two panes, the Metric component area on the top and the Definition pane on the bottom. The Metric component pane displays the complete metric definition, including its formula and calculation level, condition, and transformation components. When you select Condition in the Metric component pane, the Definition pane displays the conditions for the metric, as shown below.
The steps below show you how to use the Metric Editor to create conditional metrics. The Metric Editor can be used to modify simple and compound metrics.
Rather than using the Metric Editor to apply a filter to a single metric, you can use the Advanced Metric Assistant to combine multiple, simple metrics with multiple filters. This can help reduce the time required to create the conditional metrics for a project, as described in Creating Metrics by Combining Metrics, Filters, and Transformations.
You can also create, edit, or delete multiple metrics at the same time by using a Command Manager script. Command Manager is a MicroStrategy tool designed to automate certain tasks and processes. For more information about Command Manager, including steps to use Command Manager scripts, see the Command Manager chapter of the System Administration Help.
To Create a Conditional Metric
- In MicroStrategy Developer, choose File > New > Metric.
If the New Metric dialog box is displayed, click the Empty Metric icon. If you do not want this dialog box to be shown in the future, select Don't show this dialog in the future. Click OK. For a full description of object templates, including a list of the objects that can use object templates, see Re-Using Objects Via Shortcuts and Object Templates .
-
Create the metric formula by adding facts, attributes, metrics, operators, and/or functions.
To create the Paid Salary metric shown above, add the Compensation Cost fact from the Object Browser. The Sum function is automatically added. For detailed procedures to create basic metrics, see the Building Query Objects and Queries, for Designers chapter in the Basic Reporting Help.
You can set conditionality for simple metrics but not for compound metrics. The formula of a simple metric is based on group functions (such as sum or average). For a quick review of simple metrics and formulas, see Before You Begin. For a more detailed description of simple metrics, including examples, see the Basic Reporting Help.
- Click Condition on the Metric component pane.
- Select the filter or prompt to place on the metric using one of the following methods:
- Use the Object Browser to locate the object, then drag it into the Condition definition pane.
-
Click Browse. The Select a Filter dialog box opens, allowing you to select a filter from the displayed list, or navigate to locate the correct filter.
To see object prompts in the dialog box, select Object Prompt in the Objects of type list. Only an object prompt, which allows you to choose a filter, can be used as a metric condition.
- Select a filter or prompt and click Edit if needed. After you complete your changes, click Save and Close (in the Filter Editor) or Finish (in the Prompt Generation Wizard).
- Select a filter and click Clear to remove a filter.
- Save the metric.
The Advanced button accesses the Condition advanced options dialog box. The advanced options govern the interaction of conditional metrics and report filters, as described in Conditional Metric and Report Filter Interactions, Conditional Metric and Report Filter Interactions and Conditional Metric and Report Filter Interactions.
