Strategy ONE
HeteroscedasticTTest and HomoscedasticTTest
Return the P-value for the hypothesis test. These two functions are used to determine the level of variance between the means of paired samples, assuming both samples have different arguments. For example, they may be used when a given group is to be tested before and after an experiment.
| Decision
|
Reality: H0 is correct | Reality: H1 is correct |
|
Accept H0 |
No problem |
Type 1 error |
|
Reject H0 |
Type 2 error |
No problem |
Definition

P-value is a probability of making a Type 2 error.
HeteroscedasticTTest or HomoscedasticTTest returns the p-value for the hypothesis test in the following form:
-
For H0:
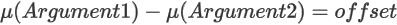
-
For H1:

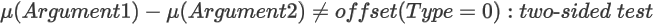

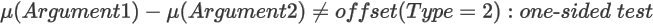
Syntax
HeteroscedasticTTest or HomoscedasticTTest <Hypothesis type, offset> (Argument1, Argument2)
Usage Notes
Heteroscedastic t-tests are based on the assumption that variances between two sample data ranges are unequal [σ2(Argument1) ¹ σ2(Argument2)].
Homoscedastic t-tests are based on the assumption that variances between two sample data ranges are equal [σ2(Argument1) = σ2(Argument2)].
The following conditions are invalid:
- Argument1 and Argument2 have a different number of data points, and Hypothesis type = 1 (paired).
- Offset or Hypothesis type is nonnumeric.
Example
For an example using both Heteroscedastic T-test and Homoscedastic T-test, see Hypothesis Testing example.
