Strategy ONE
Web Beans and Web Components
The MicroStrategy Web page can be broken into different GUI components that are placed on the page and rendered according to the rules in the Page Configuration file. This section of the MSDL discusses Web Beans and other Web GUI Components that are included within a MicroStrategy Web page.
Web Beans represent blocks of MicroStrategy data, such as report data or the contents of a folder. To render MicroStrategy data for display on a page, you use either Web Beans themselves or Web GUI Components, which represent bean/style combinations. There are two general steps in presenting data for display:
-
In the Page Configuration file, define the <web-bean> in the <page> where the bean data will be rendered. If a Web GUI Component will be used to render the data, define the <web-component> in the <template> for the appropriate <page>.
-
In the JSP or ASP.NET file for the <page-section> in the <template> where the data will be rendered, use either the <web:displayBean> or <web:displayGuiComponent> MicroStrategy custom tag to render the data.
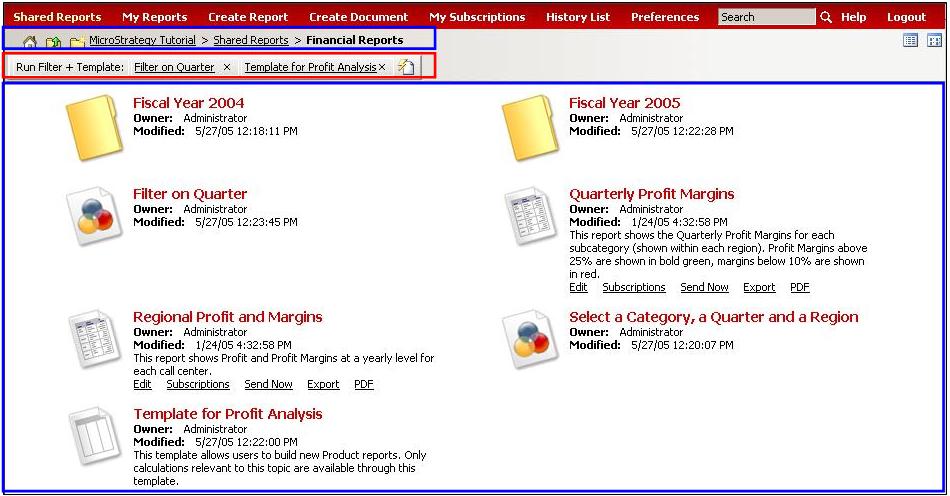
The following image shows the Folder Browsing page in MicroStrategy Web. It uses two Web Beans to display the information.
The blue rectangles show the results of a metadata bean of type FolderBean rendered using two transforms. This bean is employed two distinct times, each time with a different transform. Each transform provides unique rules for extracting relevant data from the bean and rendering it on the page.
The role of metadata beans is to contain complete access to all of the data associated with a specified MicroStrategy object. Metadata beans are also called Web beans, as they implement the WebBean interface. All Web beans are transformable (that is, they implement the Transformable interface). Transformable objects generally contain data that can be transformed, or rendered, by transform objects. Different transforms contain different rules for rendering data structures. Examples of metadata beans include FolderBeans, ReportBeans, and PromptsBeans.
The red rectangle displays the results of an application bean of type TemplateFilterExecBean rendered using one transform. Some application beans take transforms; others are self-rendering. This bean is responsible for providing an interface for selecting a template and filter to execute a report.
An application bean is related to accessing some kind of Web application functionality. For example, the sorting of report data is performed in the Sort Editor. The Sort Editor functionality and interface are stored in the SortEditorBean application bean. Many application beans such as GridFormatEditorBean and ObjectBrowserBean are not transformable but are self-rendering and automatically rendered. Many application beans that are contained by the ReportFrameBean do not work outside the context of this container. To learn about container beans, refer to the Container beans section..
See also
-
Architecture: Application objects layer
-
Architecture: Web beans layer
-
Fundamentals of customization: Types of beans in MicroStrategy Web
