Strategy ONE
Metrics with default dynamic aggregation functions
A metric defined with functions such as Sum or Product can be dynamically aggregated because these functions can be calculated at a higher level than the initial calculation. Any metric defined with one of the following functions has a default dynamic aggregation function that allows the data for the metric to be aggregated at different levels on the fly:
-
Sum or Count: Sum is used as the aggregation function.
If the Count function is set to count distinct entries, it cannot use Sum as its dynamic aggregation function and returns null values instead. The exception is for a count distinct function in a shortcut metric defined in a report, document, or Visual Insight quick dashboard created in MicroStrategy Web. For instructions to create a shortcut metric, which is a type of derived metric, see the Strategy Web Help.
- Minimum: Minimum (Min) is used as the aggregation function.
- Maximum: Maximum (Max) is used as the aggregation function.
- Product: Product is used as the aggregation function.
For example, consider the Dynamic Aggregation - Region - Employee report from the MicroStrategy Tutorial project. To focus only on those metrics that have default dynamic aggregation functions, move the metrics Standard Deviation of Revenue and Count Distinct (Items Sold) to the Report Objects pane (for steps, see Using dynamic aggregation). The report results for the Central and Mid-Atlantic regions are shown below.
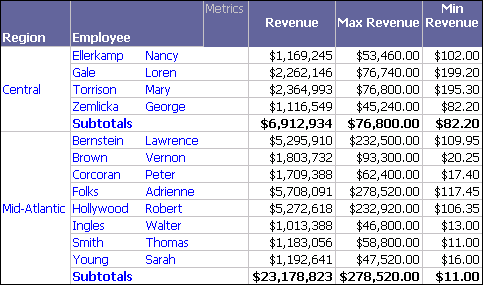
A custom subtotal has been included on this report to display subtotals for the different revenue calculations. For information on creating custom subtotals, see the Advanced Reporting Help.
The Revenue, Max Revenue, and Min Revenue metrics use total, maximum, and minimum subtotals respectively. These are the same default dynamic aggregation functions that are used for these three metrics because they are built with the Sum, Max, and Min functions respectively. You can verify that this is true by moving Employee to the Report Objects pane, which triggers dynamic aggregation, causing the metrics to be aggregated at the regional level.
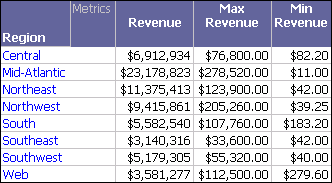
Notice that the values for the Northeast and Mid-Atlantic regions are the same values as the regional subtotals in the report prior to triggering dynamic aggregation. When the three metrics are aggregated at the regional level, each metric uses its default dynamic aggregation function to perform the calculation.
