Strategy ONE
编写 Python 数据源脚本
从 MicroStrategy ONE 开始 更新 11,要使用 Python 数据源,您必须编写一个 Python 脚本,用作数据源的连接。
数据源脚本函数
您必须在数据源脚本中使用以下三个函数:
-
browse()复制def browse():
"""
Description: retrieve the catalog information.
Input: no input is needed for this function.
Return: the result is returned as a dict object.The keys of the dict should be
table names of the python data source, and the values are normalized in Pandas
DataFrame format. Each DataFrame value will contain a table's column infos.
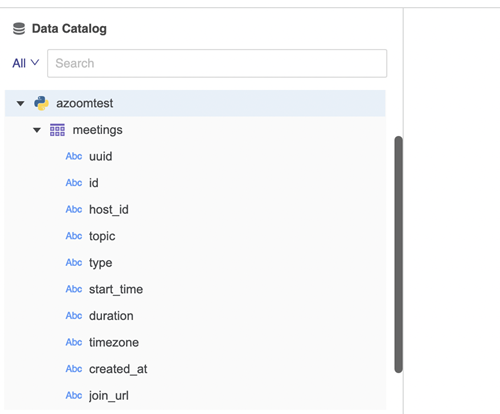
"""当用户尝试通过 python 连接器连接数据源时,会触发此浏览功能。当数据源连接时,返回该数据源的所有目录信息。表名和列显示在数据源下方。
-
preview()复制def preview(table_name, row_limit):
"""
Description: get partial data for preview, data refine and schema change
Input: there are 2 parameters for preview.
- table_name: a table name should be selected if someone want to preview
the table.
- row_limit: the row limitation is used to define the scale when only
partial data is retrieved during the preview.
Return: the result is returned as a Pandas DataFrame format object. Only the
"row_limit" rows would be returned in the DataFrame object.
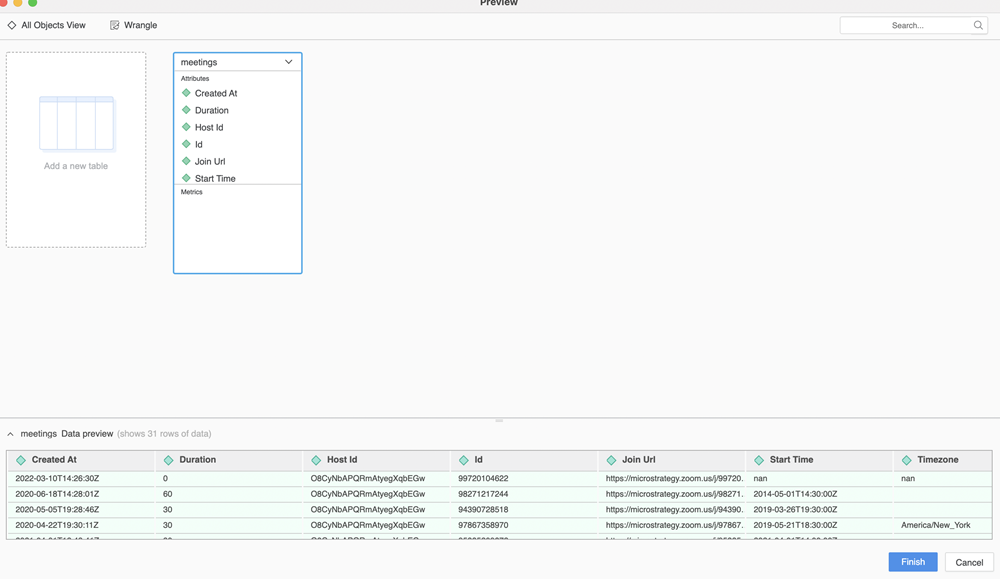
"""当用户双击添加表格或者单击预览表格时,会触发预览功能。
-
publish()复制def publish(table_name):
"""
Description: get the data published and stored the data into the cube
Input: the table_name parameter is needed to define witch table should
be published.
Return: the result is returned as a Pandas DataFrame format object. All
data needs to be returned for publishing.
"""当用户单击“保存”发布多维数据集时,将触发发布功能。检索表中的所有数据以供用户使用。
有关 Pandas DataFrame 的更多信息,请参阅10 分钟到熊猫。
数据源脚本示例
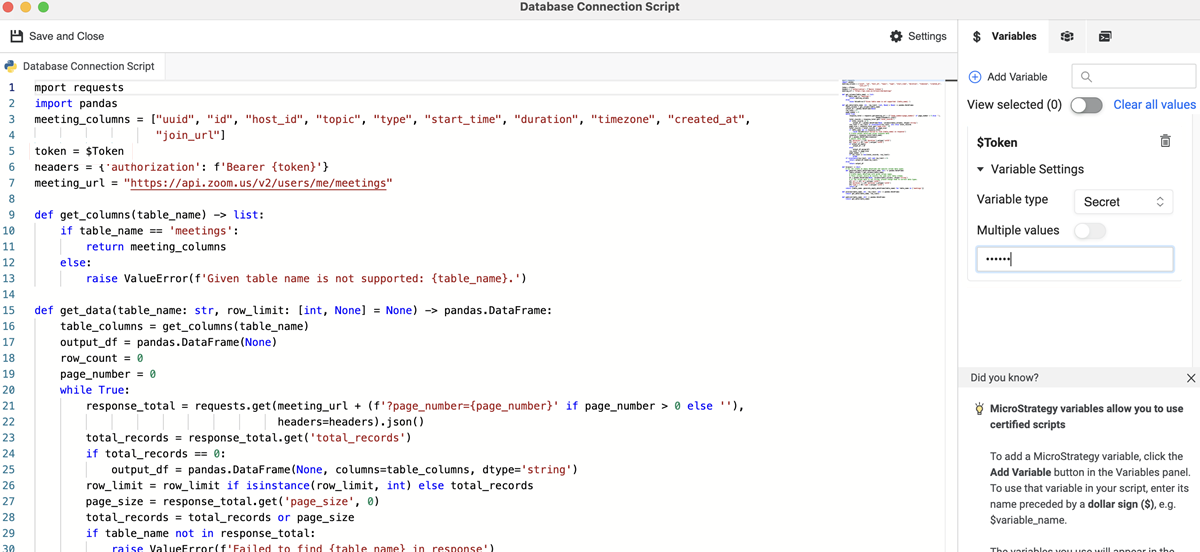
请参阅以下缩放连接器示例。用户可以使用 Python 数据源中的 API 连接到缩放资源,以检索他们想要的任何数据。该示例在数据源脚本中包含一个名为 Token 的变量,用于身份验证。
import requests
import pandas
meeting_columns = ["uuid", "id", "host_id", "topic", "type", "start_time", "duration", "timezone", "created_at",
"join_url"]
token = $Token
headers = {'authorization': f'Bearer {token}'}
meeting_url = "https://api.zoom.us/v2/users/me/meetings"
def get_columns(table_name) -> list:
if table_name == 'meetings':
return meeting_columns
else:
raise ValueError(f'Given table name is not supported: {table_name}.')
def get_data(table_name: str, row_limit: [int, None] = None) -> pandas.DataFrame:
table_columns = get_columns(table_name)
output_df = pandas.DataFrame(None)
row_count = 0
page_number = 0
while True:
response_total = requests.get(meeting_url + (f'?page_number={page_number}' if page_number > 0 else ''),
headers=headers).json()
total_records = response_total.get('total_records')
if total_records == 0:
output_df = pandas.DataFrame(None, columns=table_columns, dtype='string')
row_limit = row_limit if isinstance(row_limit, int) else total_records
page_size = response_total.get('page_size', 0)
total_records = total_records or page_size
if table_name not in response_total:
raise ValueError(f'Failed to find {table_name} in response')
# Create pandas dataframe using response data
response = response_total[table_name]
df = pandas.DataFrame(response)
# Adjust data types
df['duration'] = df['duration'].astype('int32')
df['type'] = df['type'].astype('int32')
if output_df.empty:
output_df = df
else:
output_df.merge(df)
row_count += page_size
page_number += 1
if row_count >= min(total_records, row_limit):
break
if isinstance(row_limit, int) and row_limit > 0:
return output_df.head(row_limit)
else:
return output_df
def browse() -> dict:
# You can create an empty dataframe and specify column data types.
def generate_empty_dataframe(table_name: str) -> pandas.DataFrame:
table_columns = get_columns(table_name)
# Create empty dataframe with given column names.
# These columns should be exactly the same with table schema.
df = pandas.DataFrame(None, columns=table_columns, dtype='string')
# If the column data is not string, please change them to correct data types.
df['id'] = df['id'].astype('int64')
df['duration'] = df['duration'].astype('int32')
df['type'] = df['type'].astype('int32')
return df
return {table_name: generate_empty_dataframe(table_name) for table_name in ['meetings']}
def preview(table_name: str, row_limit: int) -> pandas.DataFrame:
return get_data(table_name, row_limit)
def publish(table_name: str) -> pandas.DataFrame:
return get_data(table_name)