Version 2021
Query Optimization
This topic discusses the following types of query optimizations:
SQL Global Optimization
This setting can substantially reduce the number of SQL passes generated by MicroStrategy, to eliminate unused SQL passes, reuse redundant SQL passes, and combine SQL passes where the SELECT or WHERE clause is different. In MicroStrategy, SQL Global Optimization reduces the total number of SQL passes at the following five optimization levels:
-
Level 0: No optimization: SQL queries are not optimized.
-
Level 1: Remove Unused and Duplicate Passes: Redundant, identical, and equivalent SQL passes are removed from queries during SQL generation.
-
Level 2: Level 1 + Merge Passes with Different SELECT: Level 1 optimization takes place as described above, and SQL passes from different SELECT statements are consolidated when it is appropriate to do so.
-
Level 3: Level 2 + Merge Passes, which only hit DB tables, with Different WHERE: Level 2 optimization takes place as described above, and SQL passes which access database tables with different WHERE clauses are consolidated when it is appropriate to do so.
-
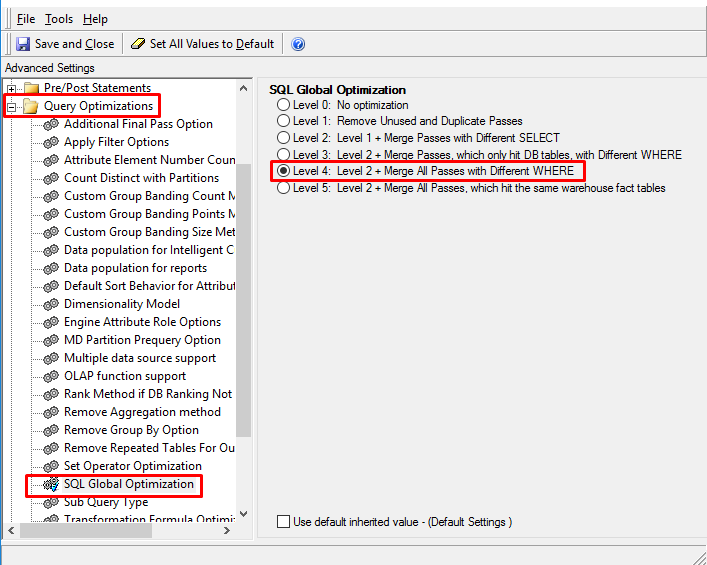
Level 4: Level 2 + Merge All Passes with Different WHERE: This is the default level. Level 2 optimization takes place as described above, and all SQL passes with different WHERE clauses are consolidated when it is appropriate to do so. While Level 3 only consolidates SQL statements that access database tables, this option also considers SQL statements that access temporary tables, derived tables, and common table expressions.
-
Level 5: Level 2 + Merge All Passes, which hit the same warehouse fact tables: Level 2 optimization takes place as described above, and when multiple passes hit the same fact table, a compiled table is created from the lookup tables of the multiple passes. This compiled table hits the warehouse fact table only once.
The default setting for PostgreSQL is to enable SQL Global Optimization at Level 4. The setting can be changed on the project level:
-
Right-click the target project > Project Configuration.
-
Select SQL Data warehouse from categories and click VLDB Properties for the target project DB instance.
-
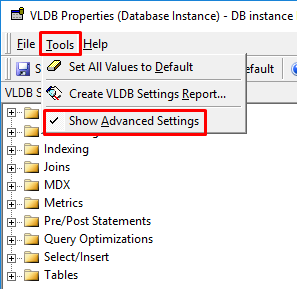
Go to Tools and select Show Advanced Settings.
-
Then the different levels of the setting can be selected as below:
Related Articles
Set Operator Optimization
This setting is used to combine multiple subqueries into a single subquery using set operators (for example, UNION, INTERSECT, EXCEPT). The default setting for PostgreSQL is to enable Set Operator Optimization.
The following is an example SQL command that displays this.
select a11.CUSTOMER_ID CUSTOMER_ID,
a11.TOT_DOLLAR_SALES WJXBFS1
from CUSTOMER_SLS a11
join LU_CUSTOMER a12
on (a11.CUSTOMER_ID = a12.CUSTOMER_ID)
where (a11.CUSTOMER_ID)
in (((select r12.CUSTOMER_ID
from ORDER_DETAIL r11
join LU_ORDER r12
on (r11.ORDER_ID = r12.ORDER_ID)
where r11.ITEM_ID in (2))
intersect (select r12.CUSTOMER_ID
from ORDER_DETAIL r11
join LU_ORDER r12
on (r11.ORDER_ID = r12.ORDER_ID)
where r11.ITEM_ID in (3))))Related Article
Parameterized Queries
Parametrized queries are available starting in MicroStrategy 2021. Parametrized queries are SQL queries that can use placeholders for data. Using placeholders allows these queries to be re-used. See KB484512 for details. The following is an example of a parameterized query
selectdistinct "a11"."CUSTOMER_ID" "CUSTOMER_ID",
CONCAT("a11"."CUST_LAST_NAME", "a11"."CUST_FIRST_NAME") "CustCol_12"
from"lu_customer""a11"
whereCONCAT("a11"."CUST_LAST_NAME", "a11"."CUST_FIRST_NAME") like ?
with parameters:
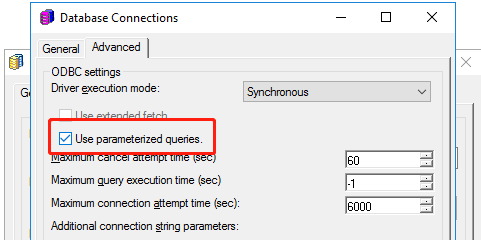
%?%Starting in MicroStrategy 2021, parameterized queries are turned on by default. You can enable or disable this feature in the Database Connections dialog, as shown below.
Select the Use parameterized queries checkbox.