MicroStrategy ONE
Using the text-based Command Manager interface
In addition to the graphical user interface and the command line execution, Command Manager has a text-based command line interface. With this interface, you can create and execute Command Manager scripts in an environment where the graphical user interface is unavailable, such as when accessing a UNIX computer via telnet.
The command-line interface has two modes:
-
Console mode, in which you can connect to a server, load a script, and change environment settings.
-
Edit mode, in which you can create, save, and execute scripts.
When you start the command line interface, it is in console mode, with a connection-less project source connection. The command prompt in console mode displays the metadata source and user to which Command Manager is connected. If it is using a connection-less connection, it reads "Not Connected-MSTR" for a connection-less project source connection, or "Not Connected-NCS" for a connection-less Narrowcast Server connection.
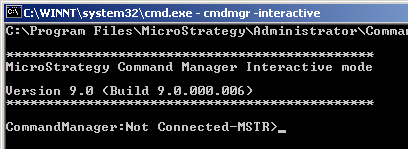
Entering a Command Manager script instruction switches Command Manager into edit mode. From edit mode you can continue typing your script. You can also save or execute the script. For more information on edit mode, see Editing, saving, and executing a script.
To start the Command Manager command-line interface
-
From the Windows Start menu, choose Run.
-
Type cmd and press ENTER. A command line window opens.
-
Navigate to the directory that contains Command Manager. By default, this is C:\Program Files\MicroStrategy\Command Manager\Command Manager.
-
Type cmdmgr -interactive and press ENTER. The command line interface opens, in console mode, with an active connection-less project source connection.
To see a list of instructions for the command-line interface
Type help and press ENTER. A list of Command Manager command line instructions and an explanation of their effects is displayed.
To exit Command Manger
Type quit and press ENTER. Command Manager exits.
